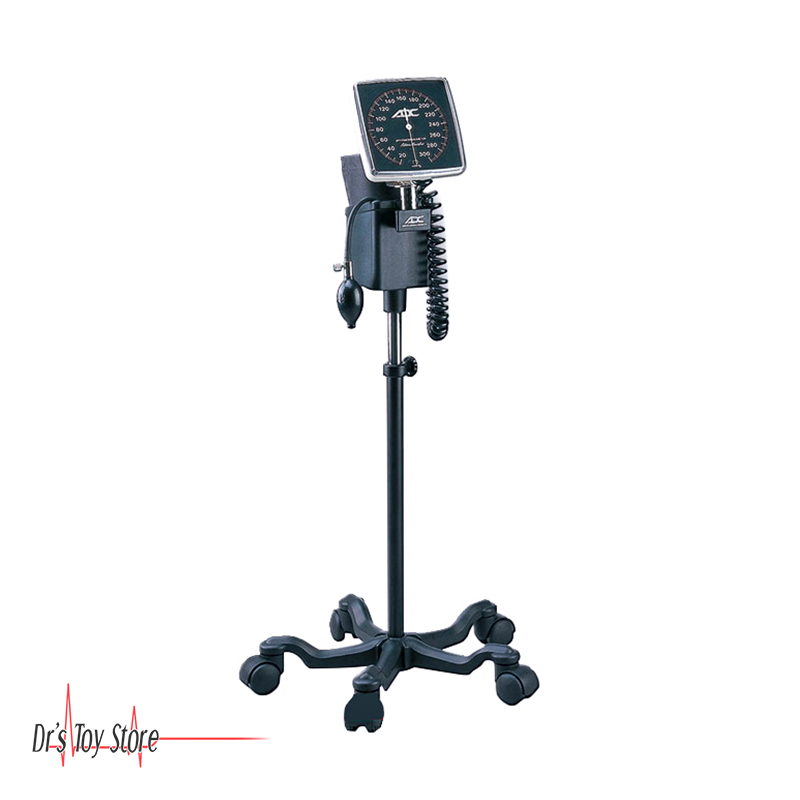
DTS Mobile Aneroid Sphygmomanometer
The DTS Mobile Aneroid Sphygmomanometer is available today at The Doctor’s Toy Store at a discount price that should cause many doctors looking to replace their existing Blood Pressure tools with this one right now. It’s on a mobile stand that makes it easy to navigate it around your practice group office or healthcare facility.
Features:
- 6″ Luminescent dial
- Adcuff inflation system
- Adflow bulb & valve
- Eight-foot coiled tubing
A sphygmomanometer, also known as a blood pressure meter, blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury or mechanical manometer to measure the pressure. It is always used in conjunction with a means to determine at what pressure blood flow is just starting, and at what pressure it is unimpeded. Manual sphygmomanometers are used in conjunction with a stethoscope.
A sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable cuff, a measuring unit (the mercury manometer, or aneroid gauge), and a mechanism for inflation which may be a manually operated bulb and valve or a pump operated electrically.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer Types
Manual
Manual meters are used by trained practitioners, this only yields the systolic pressure.
- Aneroid sphygmomanometers (mechanical types with a dial) are in common use; they may require calibration checks, unlike mercury manometers. Aneroid sphygmomanometers are considered safer than mercury sphygmomanometers, although inexpensive ones are less accurate. A major cause of departure from calibration is mechanical jarring. Aneroids mounted on walls or stands are not susceptible to this particular problem.
Digital
Digital meters employ oscillometric measurements and electronic calculations rather than auscultation. They may use manual or automatic inflation, but both types are electronic, easy to operate without training, and can be used in noisy environments. They measure systolic and diastolic pressures by oscillometric detection, employing either deformable membranes that are measured using differential capacitance, or differential piezoresistance, and they include a microprocessor. They accurately measure mean blood pressure and pulse rate, while systolic and diastolic pressures are obtained less accurately than with manual meters, and calibration is also a concern. The oscillometric method of detection used gives blood pressure readings that differ from those determined by auscultation, and vary according to many factors, such as pulse pressure, heart rate and arterial stiffness, although some instruments are claimed also to measure arterial stiffness, and some can detect irregular heartbeats.
✔ REMEMBER: WE CAN TRADE OR PURCHASE YOUR UNWANTED MEDICAL EQUIPMENT. Click here for more information.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.